02_Mybatis源码-基础包
一、源码阅读
基础包分为exception包、reflection包、annotations和lang包、type包、io包、logging包、parsing包
1.1 exception包
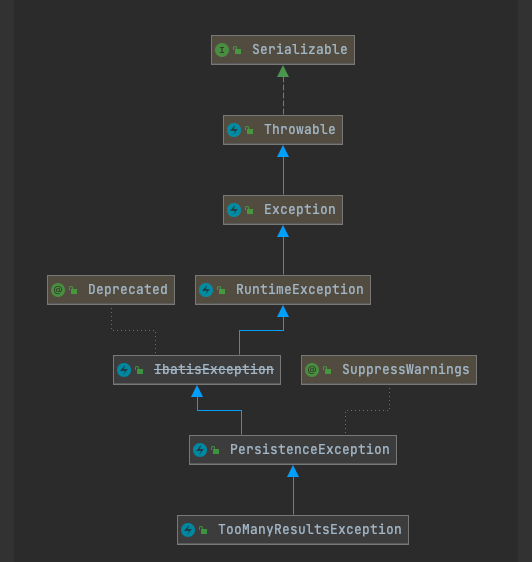
// 异常工厂用于生产PersistenceException,构造器私有化。只能通过静态方法使用
ExceptionFactory
// 继承RuntimeException 已弃用
IbatisException
// 继承IbatisException
PersistenceException
// 继承PersistenceException
TooManyResultsException
exception包定义了一些异常类。exception包分包的时候按照类型划分定义了PersistenceException类,其他异常都是按照功能划分定义在各个功能包中
1.2 reflection包
refection包下面就是核心反射类、反射包装类、异常拆包工具、参数名解析器、泛形解析器,之后就是子包:对象工厂子包、执行器子包、属性子包和对象包装器子包
1.2.1 对象工厂子包
主要是通过反射来生成实例化类
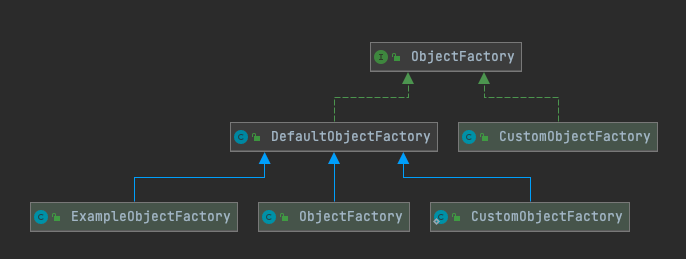
DefaultObjectFactory类代码:
// 实例化类
private <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs) {
try {
// 声明构造函数
Constructor<T> constructor;
// 如果没有参数则用无参构造器实例化
if (constructorArgTypes == null || constructorArgs == null) {
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor();
try {
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
if (Reflector.canControlMemberAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return constructor.newInstance();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
// 存在参数则用带参构造器实例化类
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor(constructorArgTypes.toArray(new Class[0]));
try {
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[0]));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
if (Reflector.canControlMemberAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[0]));
} else {
throw e;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String argTypes = Optional.ofNullable(constructorArgTypes).orElseGet(Collections::emptyList)
.stream().map(Class::getSimpleName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
String argValues = Optional.ofNullable(constructorArgs).orElseGet(Collections::emptyList)
.stream().map(String::valueOf).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
throw new ReflectionException("Error instantiating " + type + " with invalid types (" + argTypes + ") or values (" + argValues + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
1.2.2 invoker子包
主要是用反射对对象进行封装实现对象方法的调用和对象属性的读写
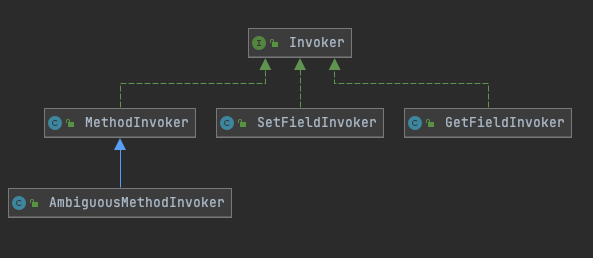
/**
* 调用接口有两个方法,一个是获取类型,一个是调用
* 实现对象方法的调用和对象属性的读写
*/
public interface Invoker {
Object invoke(Object target, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException;
Class<?> getType();
}
// GetFieldInvoker获取字段属性值的调用方法,其他继承类代码类似
@Override
public Object invoke(Object target, Object[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
try {
// 通过反射获取目标属性值
return field.get(target);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
if (Reflector.canControlMemberAccessible()) {
// 如果抛出IllegalAccessException异常则将属性的可访问性修改为可访问后重新获取
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(target);
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
1.2.3 property子包
完成对象属性的操作
// 属性复制,将一个对象的属性复制到另一个对象
PropertyCopier
// 将方法名称转为属性字段(getName > name)
PropertyNamer
// 解析student[sid].name格式的数据
PropertyTokenizer
1.2.4 wapper子包
对各种类型的对象进行包装,增加一些功能
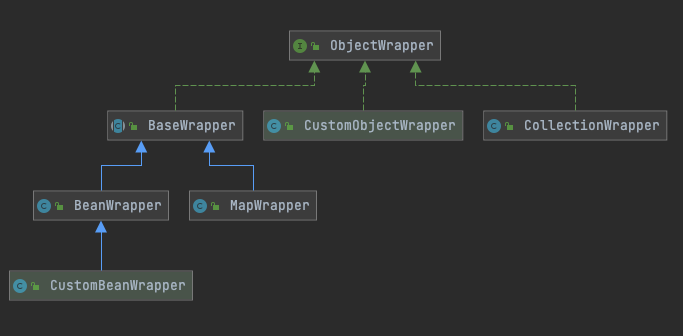
// 增加的功能如下:
public interface ObjectWrapper {
// 获得被包装对象某个属性的值
Object get(PropertyTokenizer prop);
// 设置被包装对象某个属性的值
void set(PropertyTokenizer prop, Object value);
// 找到对应的属性名称
String findProperty(String name, boolean useCamelCaseMapping);
// 获得所有的属性 get方法名称
String[] getGetterNames();
// 获得所有的属性 set方法名称
String[] getSetterNames();
// 获得指定属性的 set方法的类型
Class<?> getSetterType(String name);
// 获得指定属性的 get方法的类型
Class<?> getGetterType(String name);
// 判断某个属性是否有对应的 set方法
boolean hasSetter(String name);
// 判断某个属性是否有对应的 get方法
boolean hasGetter(String name);
// 实例化某个属性的值
MetaObject instantiatePropertyValue(String name, PropertyTokenizer prop, ObjectFactory objectFactory);
// 是否是集合
boolean isCollection();
// UnsupportedOperationException 不支持操作异常
void add(Object element);
// UnsupportedOperationException 不支持操作异常
<E> void addAll(List<E> element);
}
BeanWrapper里面包含类对象信息、类型信息
1.2.5 Reflector核心反射类
核心反射类主要是将bean转换为Reflector对象,通过ReflectorFactory去生成
// 生成Reflector对象通过Class
@Override
public Reflector findForClass(Class<?> type) {
if (classCacheEnabled) {
// synchronized (type) removed see issue #461
// 生成type的Reflector对象,并存入缓存(如果没有缓存则调用Reflector的构造器)
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(reflectorMap, type, Reflector::new);
} else {
return new Reflector(type);
}
}
// ### 反射类主要字段和部分方法 ###
public class Reflector {
// 被反射的类
private final Class<?> type;
// 有get方法的属性列表
private final String[] readablePropertyNames;
// 有set方法的属性列表
private final String[] writablePropertyNames;
// set方法列表,key为属性名,value为set方法
private final Map<String, Invoker> setMethods = new HashMap<>();
// get方法列表,key为属性名,value为get方法
private final Map<String, Invoker> getMethods = new HashMap<>();
// set方法输入类型,key为属性名,value为set方法的类型(set方法的第一个参数类型)
private final Map<String, Class<?>> setTypes = new HashMap<>();
// get方法输入类型,key为属性名,value为get方法的返回值类型
private final Map<String, Class<?>> getTypes = new HashMap<>();
// 默认构造函数
private Constructor<?> defaultConstructor;
// 大小写无关的属性映射表,key为属性大写值,value为属性名
private Map<String, String> caseInsensitivePropertyMap = new HashMap<>();
public Reflector(Class<?> clazz) {
type = clazz;
// 默认构造器
addDefaultConstructor(clazz);
// 解析get方法
addGetMethods(clazz);
// 解析set方法
addSetMethods(clazz);
// 解析所有字段
addFields(clazz);
// 设置可读和可写属性
readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
writablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
// 将可读和可写属性存储caseInsensitivePropertyMap
for (String propName : readablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
for (String propName : writablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
}
private void addGetMethods(Class<?> clazz) {
Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters = new HashMap<>();
// 获取所有方法
Method[] methods = getClassMethods(clazz);
// 过滤出get方法
Arrays.stream(methods).filter(m -> m.getParameterTypes().length == 0 && PropertyNamer.isGetter(m.getName()))
.forEach(m -> addMethodConflict(conflictingGetters, PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(m.getName()), m));
// 多个疑似get方法,找出合适的那个
resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters);
}
}
1.2.5 反射包装类
元对象MetaObject是给普通对象的一个包装类,里面有大量的辅助类
public class MetaObject {
// 原始对象
private final Object originalObject;
// 对象包装器
private final ObjectWrapper objectWrapper;
// 对象工厂
private final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
// 对象包装器工厂
private final ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory;
// 反射工厂
private final ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory;
}
元类MetaClass是给对象的包装类,对类近一步封装
SystemMetaObject是一个只能使用MetaObject.forObject默认值的一个工厂
1.2.6 异常拆包工具
ExceptionUtil
/**
* 异常拆包:
* InvocationTargetException是为了解决反射方法调用的时候出现任意类型的异常, InvocationTargetException里面的target保存了原始异常
* UndeclaredThrowableException也是一个包装了其他异常的异常
*/
public static Throwable unwrapThrowable(Throwable wrapped) {
Throwable unwrapped = wrapped;
// 持续拆包,可能会出现多层包装异常
while (true) {
// 拆包 调用目标异常 获取内部异常
if (unwrapped instanceof InvocationTargetException) {
unwrapped = ((InvocationTargetException) unwrapped).getTargetException();
// 为申报抛出异常 获取未申报异常
} else if (unwrapped instanceof UndeclaredThrowableException) {
unwrapped = ((UndeclaredThrowableException) unwrapped).getUndeclaredThrowable();
} else {
// 无需拆包
return unwrapped;
}
}
}
1.2.7 参数名解析器
参数名解析器,为了确定参数的顺序,主要逻辑:
// 将参数处理后put到names
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
this.useActualParamName = config.isUseActualParamName();
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 获取所有的参数后遍历
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
// 如果存在@Param注解则用注解的value替换
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
// 非注解则获取arg(Parameter::getName)
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
if (useActualParamName) {
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
// 获取属性参数
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
Object value = args[names.firstKey()];
return wrapToMapIfCollection(value, useActualParamName ? names.get(0) : null);
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// 生成参数名 (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
1.2.8 泛形解析器
获取字段、参数、返回值的泛型类型
// 获取字段泛型
@Test
void testField_GenericField() throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = SubCalculator.class;
Class<?> declaredClass = Calculator.class;
Field field = declaredClass.getDeclaredField("fld");
Type result = TypeParameterResolver.resolveFieldType(field, clazz);
assertEquals(String.class, result);
}
// 获取返回值泛型
@Test
void testReturn_SimpleClass() throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = Level1Mapper.class;
Method method = clazz.getMethod("simpleSelect");
Type result = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, clazz);
assertEquals(Double.class, result);
}
// 获取参数值泛型
@Test
void testParam_Primitive() throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = Level2Mapper.class;
Method method = clazz.getMethod("simpleSelectPrimitive", int.class);
Type[] result = TypeParameterResolver.resolveParamTypes(method, clazz);
assertEquals(1, result.length);
assertEquals(int.class, result[0]);
}
TypeParameterResolver类有三个public方法,分别是:
// 解决字段泛型
public static Type resolveFieldType(Field field, Type srcType) {
Type fieldType = field.getGenericType();
Class<?> declaringClass = field.getDeclaringClass();
return resolveType(fieldType, srcType, declaringClass);
}
// 解决返回值泛型
public static Type resolveReturnType(Method method, Type srcType) {
Type returnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return resolveType(returnType, srcType, declaringClass);
}
// 解决参数泛型
public static Type[] resolveParamTypes(Method method, Type srcType) {
// 获取所有参数
Type[] paramTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
Type[] result = new Type[paramTypes.length];
for (int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; i++) {
result[i] = resolveType(paramTypes[i], srcType, declaringClass);
}
return result;
}
这三个方法都调用了一个核心方法
private static Type resolveType(Type type, Type srcType, Class<?> declaringClass) {
// 类型变量: Map<K,V>, KV就是类型变量
if (type instanceof TypeVariable) {
return resolveTypeVar((TypeVariable<?>) type, srcType, declaringClass);
}
// 参数类型如:Collection<String>
else if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {
return resolveParameterizedType((ParameterizedType) type, srcType, declaringClass);
}
// 包含resolveTypeVar和resolveParameterizedType的列表
else if (type instanceof GenericArrayType) {
return resolveGenericArrayType((GenericArrayType) type, srcType, declaringClass);
} else {
return type;
}
}
这些方法的返回值都是Type类型如下:
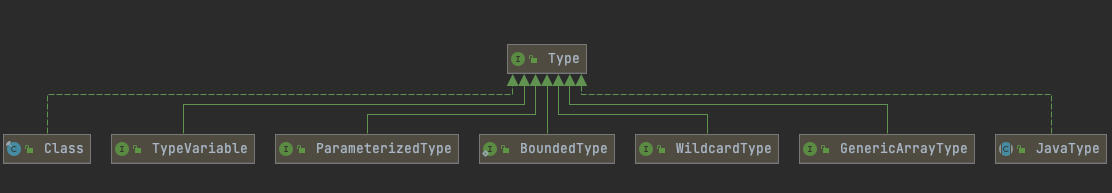
Class: java中的类和接口。如: 枚举属于类,注解是接口
WildcardType: 通配符。如: ?, ? extends Integer, ? super String
TypeVariable: 类型变量的父接口(T a)。如:Map<K,V> K V就属于类型变量
ParameterizedType: 参数化类型(泛型)。如:Collection<String> 就是参数化类型
GenericArrayType: 包含TypeVariable或ParameterizedType的列表(带有泛型的数组)
1.3 annotations和lang包
这两个包里面全是注解,理解注解即可
1.4 type包
1.4.1 分类
type包的类特别多,需要归类总结。 分为四组
- 类型处理器
- 类型处理器接口TypeHandler:定义了设置参数和获取结果的方法
- 类型参考器TypeReference:用来获取处理器是处理那一种java类型的
- 类型处理器基础实现BaseTypeHandler:利用模版方法实现了TypeHandler接口,并提供了4个抽象方法
- 43个类型处理器
- 类型注册表
- 基本类型注册表SimpleTypeRegistry: 静态方法初始化了java基本包装类型
- 类型别名注册表TypeAliasRegistry: 默认构造器注册了各种java的基本类型
- 类型处理器注册表TypeHandlerRegistry: 构造器将所有的处理器初始化到map中
- 注解类
- 别名@Alias:给类设置别名,设置之后将数据存入到TypeAliasRegistry里面
- 映射jdbc类型@MappedJdbcTypes:用自定义的处理器处理jdbc类型,创建BaseTypeHandler的子类后加上该注解
- 映射类型@MappedTypes:自定义处理java类型和MappedJdbcTypes用法一致
- 其他
- 异常类TypeException:与类型处理相关的异常
- 工具类ByteArrayUtils:数组转换工具
- 枚举类JdbcType:定义了jdbc的类型
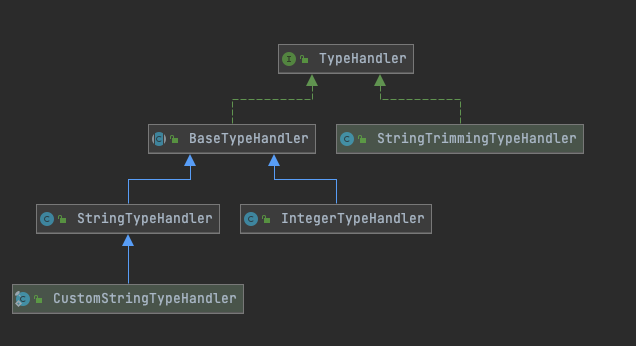
1.4.2 主要源码
整个type包比较重要的就是BaseTypeHandler,如下源码
public abstract class BaseTypeHandler<T> extends TypeReference<T> implements TypeHandler<T> {
@Deprecated
protected Configuration configuration;
@Deprecated
public void setConfiguration(Configuration c) {
this.configuration = c;
}
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (parameter == null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
throw new TypeException("JDBC requires that the JdbcType must be specified for all nullable parameters.");
}
try {
ps.setNull(i, jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different jdbcTypeForNull configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
} else {
try {
// 向PreparedStatement指定位置设置不为空的参数
setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting non null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
// 从ResultSet中通过字段名称获取可以为空的结果
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(rs, columnName);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column '" + columnName + "' from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 从ResultSet中通过字段编号获取可以为空的结果
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(rs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex + " from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 通过调用声明获取结果
@Override
public T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(cs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex + " from callable statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 向PreparedStatement指定位置设置不为空的参数
public abstract void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
// 从ResultSet中通过字段名称获取可以为空的结果
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
// 从ResultSet中通过字段编号获取可以为空的结果
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
// 从ResultSet中通过字段编号获取可以为空的结果
public abstract T getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
其他43个类都继承了BaseTypeHandler类并实现抽象方法的具体逻辑,由于BaseTypeHandler已经用模版方法模式把骨架搭好了,因此实现类的逻辑都比较简单。
1.5 io包
1.5.1 VFS
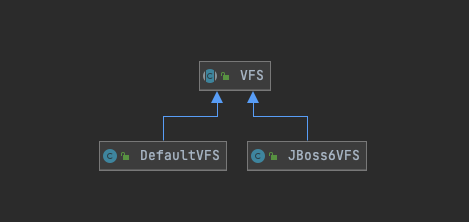
VFS主要内部类,利用单例模式找到第一个可以使用的实现类
private static class VFSHolder {
static final VFS INSTANCE = createVFS();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static VFS createVFS() {
// Try the user implementations first, then the built-ins
List<Class<? extends VFS>> impls = new ArrayList<>();
// 用户自定义的实现优先级最高
impls.addAll(USER_IMPLEMENTATIONS);
impls.addAll(Arrays.asList((Class<? extends VFS>[]) IMPLEMENTATIONS));
// 依次生成实例,找到第一个可以使用的
VFS vfs = null;
for (int i = 0; vfs == null || !vfs.isValid(); i++) {
Class<? extends VFS> impl = impls.get(i);
try {
vfs = impl.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
if (!vfs.isValid() && log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("VFS implementation " + impl.getName()
+ " is not valid in this environment.");
}
} catch (InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | NoSuchMethodException | InvocationTargetException e) {
log.error("Failed to instantiate " + impl, e);
return null;
}
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Using VFS adapter " + vfs.getClass().getName());
}
return vfs;
}
}
// 利用单利模式实现创建VFS
public static VFS getInstance() {
return VFSHolder.INSTANCE;
}
DefaultVFS.isValid默认返回true,这个实现类是在最后面的一个兜底实现。
JBoss6VFS是一个借鉴J2EE的开放源代码的JBoss6设计的一套实现类,初始化方法中会从JBoss里面加载需要的类和方法,如果不存在则将valid字段设置为false
1.5.2 类加载器
ClassLoaderWrapper是将ClassLoader包装了一下,主要逻辑如下
// 获取类加载器,前面两种可能为空,优先级由高到底
ClassLoader[] getClassLoaders(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new ClassLoader[]{
classLoader,
// 系统默认的类加载器
defaultClassLoader,
// 当前线程上下文中的类加载器
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
// 当前对象的类加载器
getClass().getClassLoader(),
// 系统类加载器
systemClassLoader};
}
// 通过5种类加载器获取文件,如果没获取到则加上/再次获取
URL getResourceAsURL(String resource, ClassLoader[] classLoader) {
URL url;
for (ClassLoader cl : classLoader) {
if (null != cl) {
url = cl.getResource(resource);
if (null == url) {
url = cl.getResource("/" + resource);
}
if (null != url) {
return url;
}
}
}
return null;
}
Resources类的属性就是ClassLoaderWrapper,之后提供各种获取资源的静态方法。
ResolverUtil类是筛选工具。判断类是否继承或实现了某个类和是否具有某个注解
1.6 loggin包
使用了适配器模式和动态代理,日志包分为两种,一种为普通的日志输出都实现了Log接口,另一种就是jdbc的日志。
1.6.1 普通Log
LogFactory去生产日志,通过静态方法去初始化,逻辑如下:
// 依次执行直到初始化日志
static {
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useSlf4jLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useCommonsLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4J2Logging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4JLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useJdkLogging);
// 兜底实现,不输出日志
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useNoLogging);
}
// 尝试实现一个日志实例
private static void tryImplementation(Runnable runnable) {
// 如果logConstructor为空的时候就去执行
if (logConstructor == null) {
try {
runnable.run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ignore
}
}
}
// 设置实现类并给logConstructor赋值
private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) {
try {
Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class);
Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
}
logConstructor = candidate;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
生产的日志都实现Log接口,一共11个实现类,实现类都很简单都是去适配了各个日志包的方法
public interface Log {
// 是否debug/Trace能力,这两个是从效率角度考虑设计的。这两个级别的日志大部分时间都是关闭状态的
// 这两个方法就可以作为日志输出的前置判断,避免浪费资源
boolean isDebugEnabled();
boolean isTraceEnabled();
void error(String s, Throwable e);
void error(String s);
void debug(String s);
void trace(String s);
void warn(String s);
}
1.6.2 jdbc日志
jdbc是具体的数据库读写操作,jdbc处理的时候mybatis是无法打印日志的。这个jdbc子包就是为了将jdbc的操作日志打印出来,实现方式是通过jdk动态代理。如下逻辑:
// BaseExecutor获取链接
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
// 如果由debug能力则通过动态代理生成Connection的代理类
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return connection;
}
}
// ##### ConnectionLogger的invoke方法,其他代理类和该方法类似 #####
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params)
throws Throwable {
try {
// 如果是类则直接执行方法逻辑
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
// 方法名为prepareStatement||prepareCall是则判断是否需要debug日志输出
if ("prepareStatement".equals(method.getName()) || "prepareCall".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Preparing: " + removeExtraWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
// 调用目标方法执行逻辑后返回一个PreparedStatement的代理类
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
}
// 方法名为createStatement则执行方法后返回一个Statement的代理类
else if ("createStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
Statement stmt = (Statement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = StatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else {
return method.invoke(connection, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
// 创建一个代理类
public static Connection newInstance(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new ConnectionLogger(conn, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = Connection.class.getClassLoader();
return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{Connection.class}, handler);
}
1.7 parsing包
1.7.1 测试通用标记解析器
// 实现标记处理器
public static class VariableTokenHandler implements TokenHandler {
private Map<String, String> variables = new HashMap<>();
VariableTokenHandler(Map<String, String> variables) {
this.variables = variables;
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
return variables.get(content);
}
}
@Test
void test(){
// 准备替换的数据
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>() {{
put("first_name", "James");
put("initial", "T");
put("last_name", "Kirk");
put("var{with}brace", "Hiya");
put("", "");
}};
// 初始化通用标记解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", new VariableTokenHandler(map));
// 断言解析结果
assertEquals("James T Kirk reporting.", parser.parse("${first_name} ${initial} ${last_name} reporting."));
assertEquals("Hello captain James T Kirk", parser.parse("Hello captain ${first_name} ${initial} ${last_name}"));
assertEquals("James T Kirk", parser.parse("${first_name} ${initial} ${last_name}"));
assertEquals("JamesTKirk", parser.parse("${first_name}${initial}${last_name}"));
assertEquals("{}JamesTKirk", parser.parse("{}${first_name}${initial}${last_name}"));
assertEquals("}JamesTKirk", parser.parse("}${first_name}${initial}${last_name}"));
}
通用标记解析器代码GenericTokenParser
// 通用标记解析
public class GenericTokenParser {
// 占位符起
private final String openToken;
// 占位符止
private final String closeToken;
// 占位符处理器
private final TokenHandler handler;
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
// 内容解析(如:将sql语句的 #{id} 解析为?)
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
do {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
} while (start > -1);
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
// 标记处理器接口
public interface TokenHandler {
String handleToken(String content);
}
上面的代码就是解析替换的主要逻辑,parsing包里面主要就是XPathParser和XNode两个类,可以分别看作javax.xml.xpath.XPath和org.w3c.dom.Node的包装类。
1.7.2 解析类
XPathParser主要代码:
public class XPathParser {
// mybatis-config.xml文件数据
private final Document document;
// 是否校验(true)
private boolean validation;
// 声明找DTD文件的方法
private EntityResolver entityResolver;
// mybatis-config里面的properties
private Properties variables;
// javax.xml.xpath.XPath工具
private XPath xpath;
// 通过表达式解析节点
public String evalString(String expression) {
return evalString(document, expression);
}
public String evalString(Object root, String expression) {
String result = (String) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.STRING);
// 属性解析器就是利用GenericTokenParser去进行文本内容解析
result = PropertyParser.parse(result, variables);
return result;
}
}
XNode主要代码
public class XNode {
// 节点
private final Node node;
// 节点名
private final String name;
// 节点体
private final String body;
// 节点属性
private final Properties attributes;
// mybatis-config里面的properties
private final Properties variables;
// 解析器(自封装解析器,可以解析自身)
private final XPathParser xpathParser;
// 其他代码都是获取各种属性值
...
}
二、包结构汇总
各个包比较重要的地方和用到的设计模式整理
| 包名 | 重点 | 设计模式 |
|---|---|---|
| exception | 分包方式和异常拆包 | 工厂模式 |
| reflection | 反射 | 装饰器模式 |
| annotations/long | 注解 | |
| type | 各个类分类/Type类 | 模版方法模式 |
| io | VFS/JBoss6 | 单例模式/静态代理 |
| logging | 日志框架和级别 | 适配器模式/动态代理 |
| parsing | xml/解析器 |