08_代词
代词可以使用来代替不同的名词,以避免重复使用特定的名词,提高语言表达的流畅性和清晰度
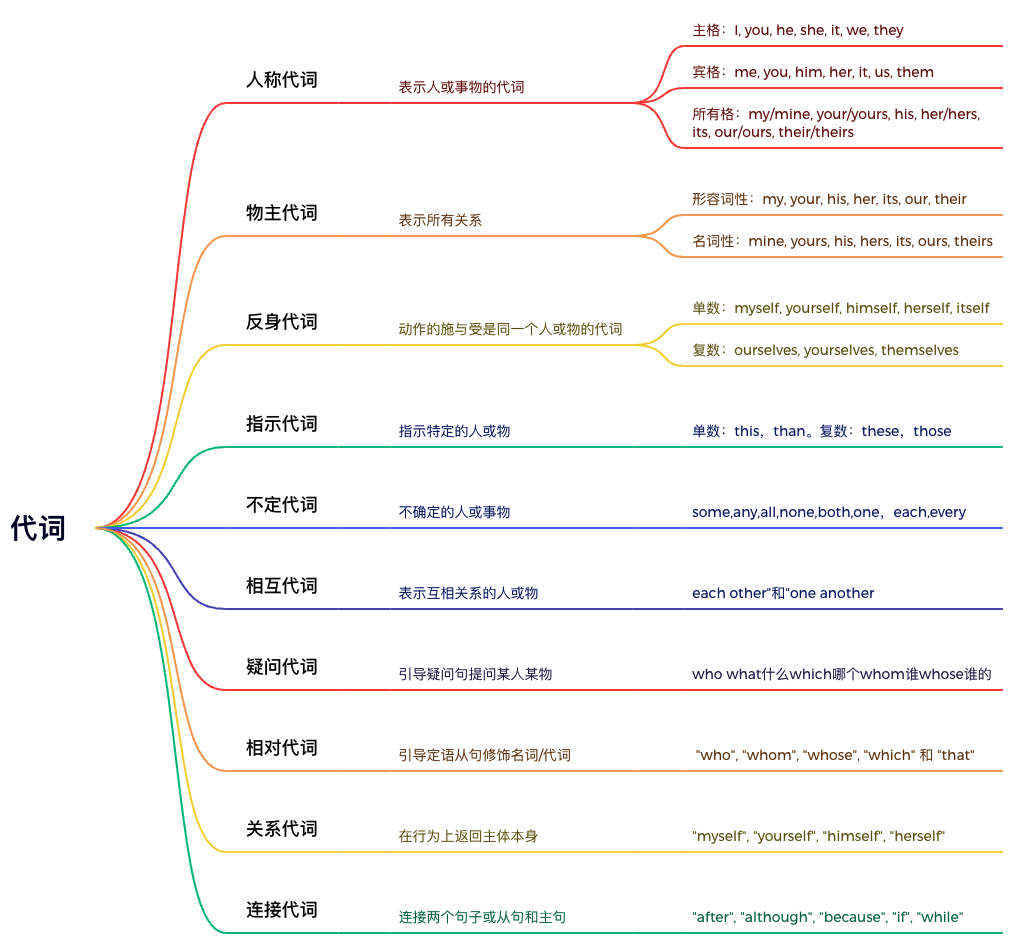
一、人称代词
用来表示人或事物的代词
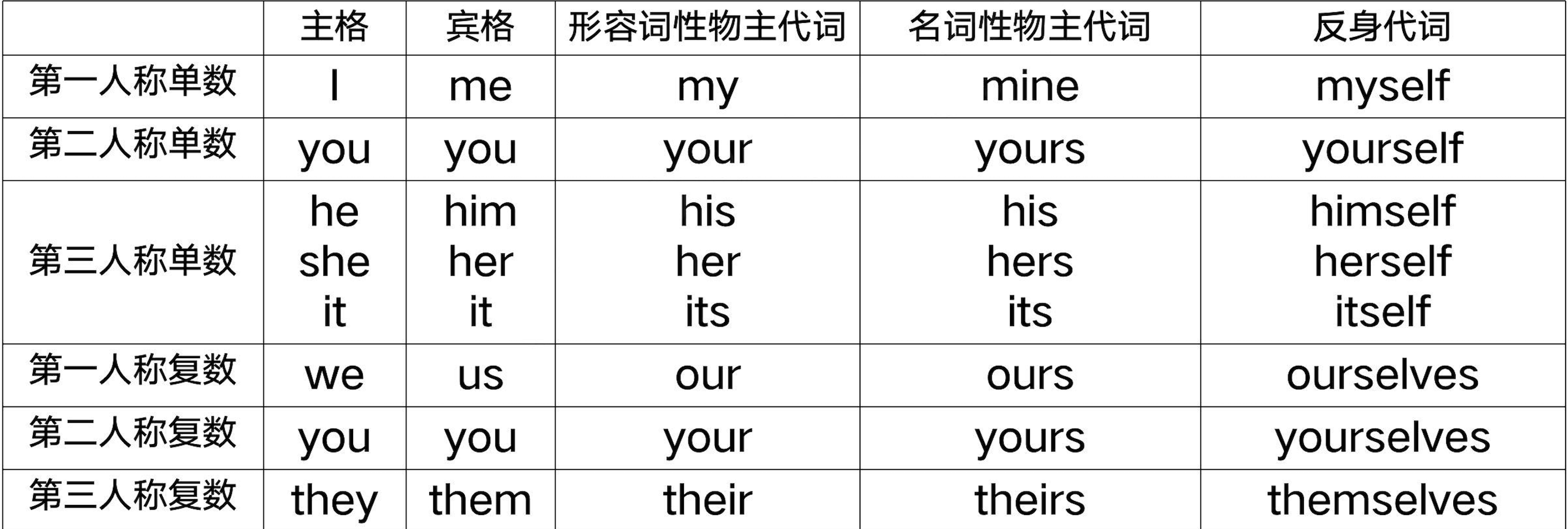
1.1 主格
在句子里做主语或者表语:I, you, he, she, it, we, they
They are students// 他们是学生
It is you // 它是你
1.2 宾格
做及物动词或者介词之后的宾语:me, you, him, her, it, us, them
I tell her my name // 我告诉她我的名字
I should apologize to her // 我应该向她道歉
1.3 所有格
my/mine, your/yours, his, her/hers, its, our/ours, their/theirs
1、使用顺序
第二人称(你) > 第三人称(他)> 第一人称(我)
You and he // 你和他
He an me // 他和我
You and he and me are all students // 你和他还有我都是学生
2、It的用法
// 天气
It is cloudy(多云)
// 时间
It is 6 o'clock(6点整)
// 距离
It is 5 miles(5英里)
//环境
It is desert(沙漠)
// 指上文提过的某物
I have a cute cat, and it has blue eyes(我有一只猫,它有蓝色的眼睛)
// 不知道性别的人
She ha a cute bady, and it has blue eyes(她有一个可爱的宝宝,宝宝有蓝色的眼睛)
// 已经发生的、正在发生的
Stop it(停下)
// 打电话分辨人
Hello, Peter, It's Jack here(你好,皮特,我是杰克)
// 做形式主语
It is confident that he will win the match(他们有信心赢得比赛)
// 做形式宾语
I realized it tough to learn ski well(我意识到学好滑雪很难)
二、物主代词
用来表示所有关系的代词
// 形容词性物主代词,做名词的修饰(的),后面加名词
She is my aunt // 她是我的姑妈
They are their cars // 他们是他们的车
// 名词性物主代词,相当于名词,表示事物又表明所属
You're not mine // 你不是我的
Your house is huge, but ours is rather samll // 你的房子很大,但是我们的反正很小
// 双重所有格,of+名词性物主代词
He is a friend of mine // 他是我的朋友
An old friend of mine // 一个我的老朋友
三、反身代词
动作的施与受都是同一个人或物的代词,表示什么...自己
// 做宾语,指一个动作反馈到动作发出者身上
Stop! You might burn yourself // 停,你可能会烧到自己
// 做同位语,表示强调,解释说明,强调名词或者代词
The book itself is interesting // 这本书很有趣
四、指示代词
说明近处远处、上下文的人或物
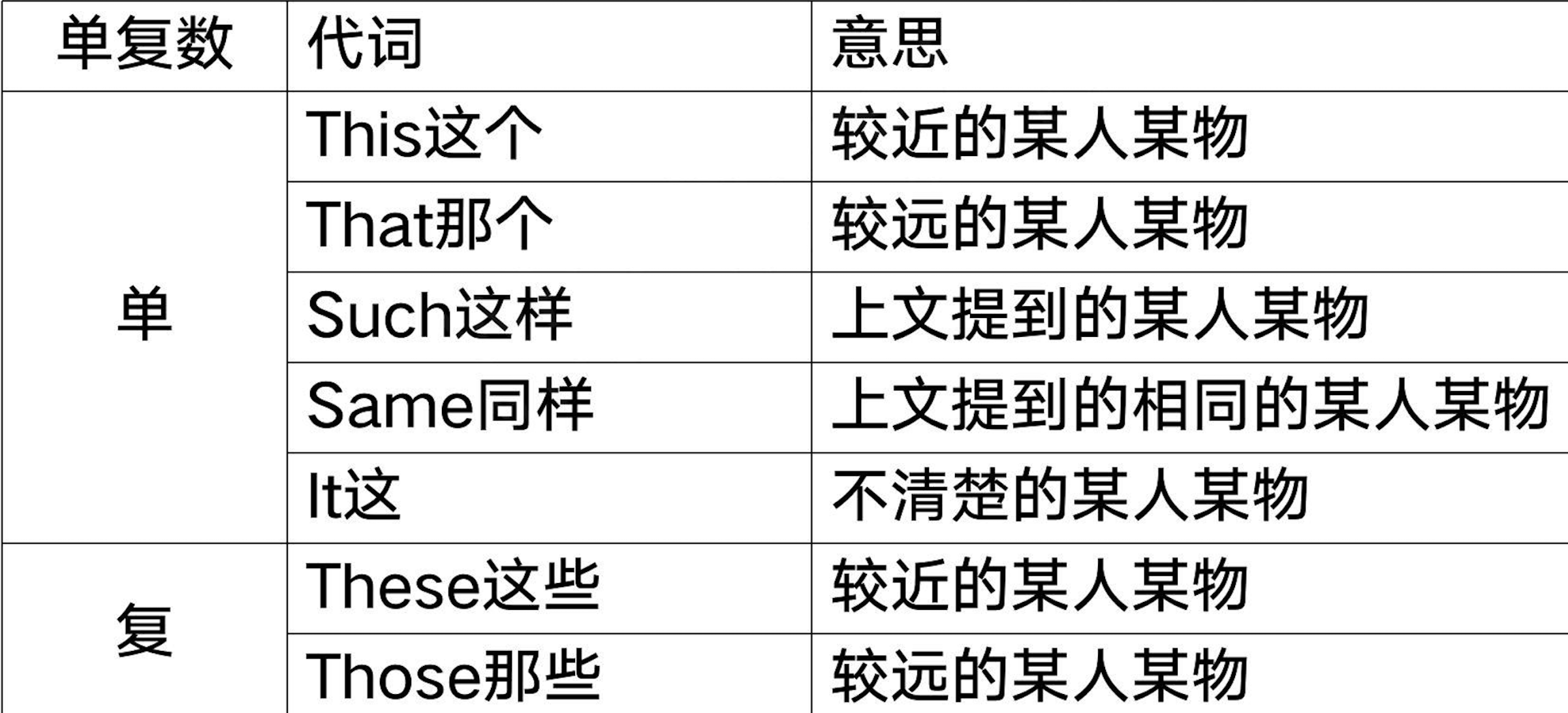
there // 副词:在那里
these // 哲这些
those // 那些
this // 这个
that // 那个
五、疑问代词
疑问代词(Interrogative Pronouns):疑问代词用于构建疑问句,通常用来提问某样东西或某个人。
常见的疑问代词包括 who谁,what什么,which哪个,whom谁,whose谁的
// 用来提出问题的代词,不分单复数,有修饰的名词决定
what, who, whose, whom, which, whatever, whichever ,whoever, whomever
六、不定代词
用来指代不确定的人或事物的代词,包括some, any, all, none, both, one, each, every等
代替或者修饰不确定的人或物,可以做主语宾语表语定语状语
// 1、 some 和 any的区别, 都可以修饰可数名词和不可数名词
// some肯定句:表示几个、一些、某个
I have some problems(我有一些问题)
// some疑问句:表示建议、请求希望
Do you want to get some drinks(你想喝点什么)
// any肯定句:表示任何的
I don't get any question(我没有遇到任何问题)
// any疑问或者否定句,表示任何一些,任何一个
Do you have any drinks(你有任何喝的吗)
// 2、 no和none的区别,都可以修饰可数名词和不可数名词
// no做定语,表示没有
We are no time(我们没有时间)
I have no answer to these(我没有回答这些)
// None做主语宾语表语,表示没有一个人/物
None escape the tomb(万物难逃一死)
None of them could escape(我们谁也跑不掉)
// 3、all和both的区别
// all指三者或者以上的人或物,可修饰可数名词和不可数名词
I knows all of the five chinese students(五个中学生我都认识)
// both指两个或者物,可修饰可数名词
They both spoke together(他们两个齐声说)
// 4、every和each的区别
// every表示每一个,指3个或3个以上的整体中的每一个,侧重于整体,形容词只能做定语,可以修饰单数名词
I eat vegetables every day(我每天都吃蔬菜)
// each表示每个各个,指两个或两个以上中的每一个,强调个别。代词作主语宾语定语
Each life is precious(每一个生命都是珍贵的)
// 5、either和neigher的区别
// either表示两个中间的任何一个
The woman was either drunk or crazy(这个女人要么喝醉了要么疯了)
// neigher表示either的否定形式,两个都不要
I know neither of them(他们两个我都不认识)
// 6、other和the other和another的区别
// other表示不同种类的另一个,其余
Do you like other styles(你喜欢其他的款式吗)
// another 表示同种类的另一个,又一个
I have another story(我有另一个故事)
// The other 表示两个里面的另一个
Why not try the other box(为什么不尝试另外一个盒子)
// 7、others和the others的区别
// others表示其余的人或物,指大部分
Some students are playing football, and others are watching them(有些学生正在踢球,其他学生在看他们踢)
// the others表示其余的人或物,指全部
John and the others are here(约翰和其他人都在这)
// 8、many和much的区别
// many表示很多,跟可数名词复数连用
I have many friends(我有很多朋友)
// much表示很多,跟不可数名词连用
I have much time(我有很多时间)
// 9、合成不定代词谓语动词用单数
some- every-开头的用在肯定句中
any-开头的用在否定句和疑问句和条件状语从句
no-开头的用在否定句中
-thing结尾指物,-one -body结尾指人
// 10、none、no one、nobody的区别
// no one和nodody指人,后面不能跟of,谓语用单数
Almost no one believed him(几乎没有人相信他)
// none指人指物,后面能跟of,谓语动词单数复数都想
None of us agreed with him(我们都不同意他的看法)
// 11、a lot of, lots of、a number of、large number of、a great deal of、plenty of的区别
// a lot of, lots of、plenty of修饰可数名词复数和不可数名词
A lot of people overlook to keep healthy(很多人忽视了保持健康)
// a number of、large number of修饰可数名词复数
A number of apples are green(一些苹果是绿色的)
// a great deal of修饰不可数名词
A great deal of time can rest(大量的时间可以休息)
// 12、few和a few和little和a little的区别
// few/a few跟可数名词连用,或者代指可数事物
// litter/a little跟不可数名词连用,或者指代不可数事物
// 否定表达: few(很少几个),little(少到几乎没有)
I have few apples(我苹果很少)
I have little water(我水很少)
// 肯定表达:a few(有几个),a little(有一些)
I have a few apples(我有几个苹果)
I have a little water(我有一点水)
七、相互代词
相互代词(Reciprocal pronouns)用来表示相互关系的人或事物,通常用于描述两个或多个人之间的相互行为或关系。
英语中的相互代词包括"each other"和"one another"。
例如:They love each other.(他们彼此相爱。)在这个句子中,"each other"表示彼此之间的相互关系。
表示相互关系的代词
You can test each other // 你可以互相考验对方
We're still attracted to one another // 我们依然喜欢彼此
八、关系代词
关系代词(Reflexive Pronouns):关系代词主要用于表示在行为上返回主体本身,通常在动词或介词后使用。
英语的关系代词包括"myself", "yourself", "himself", "herself", "itself", "ourselves", "yourselves", "themselves"。
例如:"She hurt herself during the game."(她在比赛中受伤了。)
用来引导定语从句的代词,充当定语从句成分
who指人:在定语从句作主语
whom指人:在定语从句作宾语
which指物:在定语从句作主语或者宾语
that指人:相当于who和whom
that指物:相当于which
在定语从句作主语或者宾语
九、连接代词
连接代词(Conjunctive or Subordinating Conjunctions):连接代词用于连接两个句子或连接从句和主句,以及表达时间、原因、条件、结果等关系。
常见的连接代词包括 "after", "although", "because", "if", "since", "while", "until" 等。
例如:"I will go to the party after I finish my homework."(我完成作业后会去参加派对。)
// 从引导名词性从句(主语从句,宾语从句,表语从句)
what(什么),who(谁),which(哪个),whose(谁的)等等
十、相对代词
相对代词(Relative Pronouns):相对代词用于引导定语从句,修饰名词或代词,并且在主句和从句之间建立关系。
常见的相对代词包括 "who", "whom", "whose", "which" 和 "that"。
例如:"The book that I bought is very interesting."(我买的那本书非常有趣。)
十一、其他常用
any
// 表示“任何”,可以用于否定句和疑问句中。
There isn't any water in the bottle.(瓶子里没有水。)Do you have any questions?(你有什么问题吗?)
// 表示“一些”,可以用于肯定句中。
I have some books, but I don't have any money.(我有一些书,但我没有钱。)
// 用于条件句中,表示“任何”。
If you have any problems, please let me know.(如果你有任何问题,请告诉我。)
// 与 other 连用,表示“其他任何”。
Any other questions?(还有其他问题吗?)
// 用于比较级和最高级前,表示“任何”。
She is taller than any other girl in her class.(她比她班上任何其他女孩都高。)
anyone: 任何人
anything:任何事物
anywhere:任何地方
anyhow:无论如何
any more: 再也不