01_数据结构
About 4 minstudyalgorithm
内存中存储数据的两种方式:数组和链表,总结如下:
| 结构 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| 单向链表 | 每个节点有引用指向下一个节点 |
| 双向链表 | 每个节点有指向上一个和下一个节点的引用 |
| 栈(弹夹) | 先进后出 |
| 队列(排队) | 先进先出 |
| 常见实现方式 | 实现注意点 |
|---|---|
| 数组实现栈和队列 | 数组存储数据下标记录位置,队列实现一个记录头一个记录尾即可。 循环队列两种方式: 牺牲一个位置判断,一种是利用数量标记区分 |
| 链表实现栈和队列 | 用头节点和尾节点记录即可实现 |
| 找出栈中最小值 | 利用两个栈,第二个栈一直存放最小的数据 |
| 队列实现栈 | 两个队列互相倒,最后一个就出栈 |
| 栈实现队列 | 将所有push栈里面的数据全部倒入到pop栈,pop栈为空时才倒 |
| 单链表和双链表反转 |
一、 链表
// 单链表
class OnlyNode{
private String name;
private OnlyNode next;
}
// 双链表
class DoubleNode{
private String name;
private DobleNode next;
private DoubleNode prev;
}
二、队列和栈
队列:先进先出,如排队
栈:先进后出,如弹夹
代码实现比较简单,如下:
1 链表实现队列
class LinkedQueueNode {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
private Integer size = 0;
public void push(String name) {
Node node = new Node(name);
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}
if(this.tail != null) {
this.tail.setNext(node);
}
this.tail = node;
this.size++;
}
public Node pop() {
Node head = this.head;
this.head = this.head.getNext();
head.setNext(null);
return head;
}
}
2 链表实现栈
class LinkedStack{
private Node node;
public void push(String name) {
Node node = new Node(name);
if(this.node == null){
this.node = node;
return;
}
node.setNext(this.node);
this.node = node;
}
public Node pop() {
if(this.node == null) {
return null;
}
Node next = this.node;
this.node = next.getNext();
return next;
}
}
3 数组实现栈
@Data
class ArrayStack{
private int[] stack;
private int index;
public ArrayStack(int size){
this.stack = new int[size];
this.index = 0;
}
public void push(int val) {
if(index == stack.length) {
System.out.println("满了");
return;
}
int temp = index;
this.index++;
this.stack[temp] = val;
}
public int pop(){
if(this.index == 0) {
System.out.println("没有数据了");
return -1;
}
this.index--;
return this.stack[this.index];
}
}
4 数组实现队列
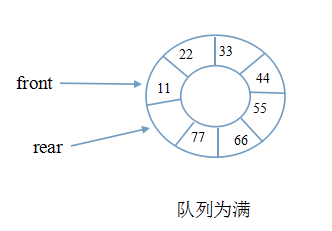
5 循环队列数组
循环数组队列:添加队列数组时只要存在空位置就可以往队列中添加元素。
/**
* 循环队列数组
*
* https://www.cnblogs.com/heliusKing/p/12326816.html
*/
class CycleQueueArray {
int querySize = 0;
int front = 0;
int rear = 0;
int[] query;
public CycleQueueArray(int querySize){
// 牺牲一个位置用于标记
querySize++;
this.querySize = querySize;
query = new int[querySize];
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
// 当队尾和队头相等时,表明为空队列
return rear == front;
}
/**
* 判断是否为满队列(当头和尾在同一个位置时,无法区分是空数组还是满了)
* 一般有两种做法:
* 1、用一个标记去记录
* 2、牺牲一个位置用来标记
*
* @return true:满
*/
public boolean isFull(){
// 表明队尾和队头相邻 且队尾在左,队头在右
return (rear + 1) % querySize == front;
}
public void push(int num){
if (isFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满 无法加入数据");
return;
}
query[rear] = num;
System.out.println((rear + 1) % querySize);
rear = (rear + 1) % querySize;
}
public int pop(){
if (isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("为空,不能取值");
}
int value = query[front];
front = (front + 1) % querySize;
return value;
}
public void showQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("为空,不能遍历");
}
for (int i = front; i < front + (rear + querySize - front) %querySize; i++){
System.out.print(query[i] + ", ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
另外一个利用字段标记实现
@Data
class ArrayQueue {
private int[] queue;
private int start;
private int end;
private int size;
public ArrayQueue(int size) {
this.start = 0;
this.end = 0;
this.queue = new int[size];
}
public void push(int val){
if(size == queue.length) {
System.out.println("满了");
return;
}
this.queue[end] = val;
this.end = end < queue.length-1 ? end+1 : 0;
this.size++;
}
public int pop() {
this.size--;
this.start = start < queue.length ? start++ : 0;
return this.queue[start];
}
}
三、其他数据结构整理
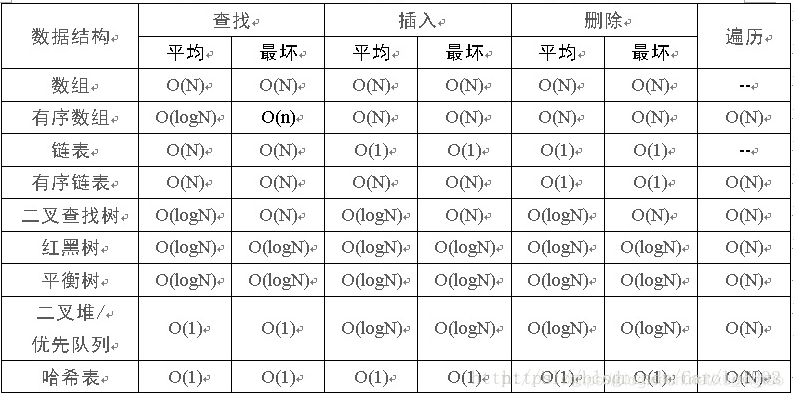
1. 常见数据结构时间复杂度
2. 常见数据结构
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 数组 array | [] |
| 队列 queue | 先进先出 |
| hash散列 | |
| 链表 link | 前后节点关联 |
| 栈 stack | 先进后出 |
| 树 tree | |
| 推 heap | |
| 图 graph |
3. 常见Tree
| 名称 | 解决什么问题 | 如何解决 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 二叉树 | 解决链表深度问题 | 任意节点最多包含两个节点 | 可能出现斜树 |
| 平衡二叉树(AVL) | 解决斜树 | 修改树平衡(左右树高度<=1),左旋/右旋 | 节点操作复杂,插入删除频繁不适合 |
| 红黑树 | 解决增删多问题 | 通过红黑节点处理 | 适合内存查询,不适合文件 |
| B树 | 做文件系统的索引 | 多路存储,降低树的深度。 | 每个节点都有数据,磁盘io多 |
| B+树 | 解决每个节点都有数据问题 | 叶子结点包含所有数据,双向链表 |
四、递归
- 任何递归都可以用函数改为非递归
- 符合固定格式的递归