04_二叉树学习
一、链表递归实现先序、中序、后序
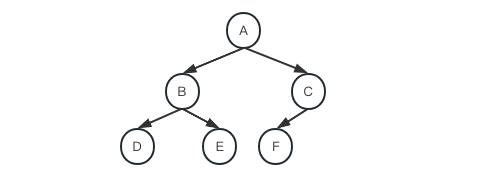
遍历的先序中序后序是按照头节点在前面、中间、后面区分的。分别为:
先序:头、左、右,上图遍历顺序ABDECF
中序:左、头、右,上图遍历顺序DBEAFC
后序:左、右、头,上图遍历顺序DEBFCA
// 先序打印所有节点
public static void pre(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println(head.value);
pre(head.left);
pre(head.right);
}
public static void in(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
in(head.left);
System.out.println(head.value);
in(head.right);
}
public static void pos(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
pos(head.left);
pos(head.right);
System.out.println(head.value);
}
二、链表非递归实现先序、中序、后序
先序
1、利用栈实现将头、右、左(元素不为空)依次push到栈中
2、循环弹出的值就是先序
// 先序遍历打印
public static void pre(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(node);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node pop = stack.pop();
System.out.print(pop.val);
if(pop.right != null) {
stack.push(pop.right);
}
if(pop.left != null) {
stack.push(pop.left);
}
}
}
中序
1、先将所有的左子节点入栈,到null为止
2、从栈中弹出节点,并将弹出节点的右子节点作为头重复步骤1. 弹出的节点就是中序
3、栈为空停止遍历
// 中序遍历打印
public static void in(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || node != null) {
if(node != null) {
stack.push(node);
node = node.left;
} else {
node = stack.pop();
System.out.print(node.val);
node = node.right;
}
}
}
后序
1、利用栈实现先左后右(元素不为空)的push到栈中
2、循环加入到另外一个栈中
3、循环弹出第二个栈的值就是后序
// 后序遍历打印(和先序不同的就是先左在右,之后逆序输出即可)
public static void pos(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> pos = new Stack<>();
stack.add(node);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node pop = stack.pop();
pos.push(pop);
if(pop.left != null) {
stack.push(pop.left);
}
if(pop.right != null) {
stack.push(pop.right);
}
}
while (!pos.isEmpty()) {
Node pop = pos.pop();
System.out.print(pop.val);
}
}
不用两个栈的方式实现后序,极客写法
三、二叉树按层遍历

按层遍历后: ABCDEF
1、利用队列(先进先出),将二叉树数据add到队列中,并遍历队列到队列为空为止
2、二叉树的左边存在数据就先放左边的值
// 按层遍历
public static void level(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 弹出队列里面的值打印
Node poll = queue.poll();
System.out.print(poll.val);
// 队列里面的存在left|right则放入队列中
if(poll.left != null) {
queue.add(poll.left);
}
if(poll.right != null) {
queue.add(poll.right);
}
}
}
四、二叉树的序列化和反序列化
将二叉树按照节点转换成字符串,不忽视空节点。以及通过字符串转换成二叉树。
先序序列
利用先序遍历的方式序列化
// 先序序列化
public static Queue<String> preSerialize(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
pre(node, queue);
return queue;
}
private static void pre(Node node, Queue<String> queue) {
if(node == null) {
queue.add(null);
return;
}
queue.add(node.val);
pre(node.left, queue);
pre(node.right, queue);
}
// 先序反序列化
public static Node preUnSerialize(Queue<String> queue) {
if(queue == null || queue.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return pre(queue);
}
private static Node pre(Queue<String> queue) {
String poll = queue.poll();
if(poll == null) {
return null;
}
Node node = new Node(poll);
node.left = pre(queue);
node.right = pre(queue);
return node;
}
后序序列
利用后序遍历的方式序列化
// 后序序列化
public static Queue<String> posSerialize(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
pos(node, queue);
return queue;
}
private static void pos(Node node, Queue<String> queue) {
if(node == null) {
queue.add(null);
return;
}
pos(node.left, queue);
pos(node.right, queue);
queue.add(node.val);
}
// 后序反序列化
public static Node posUnSerialize(Queue<String> queue) {
if(queue == null || queue.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
stack.push(queue.poll());
}
return pos(stack);
}
public static Node pos(Stack<String> stack) {
String pop = stack.pop();
if(pop == null) {
return null;
}
Node node = new Node(pop);
node.right = pos(stack);
node.left = pos(stack);
return node;
}
按层序列
利用按层遍历的方式序列化
// 按层序列化
public static Queue<String> levelSerialize(Node node) {
Queue<String> res = new LinkedList<>();
if(node == null) {
res.add(null);
return res;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(node);
res.add(node.val);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node poll = queue.poll();
if(poll.left != null) {
queue.add(poll.left);
res.add(poll.left.val);
} else {
res.add(null);
}
if(poll.right != null) {
queue.add(poll.right);
res.add(poll.right.val);
} else {
res.add(null);
}
}
return res;
}
// 按层反序列化
public static Node levelUnSerialize(Queue<String> queue){
if(queue == null || queue.size() < 1) {
return null;
}
Node head = generateNode(queue.poll());
Queue<Node> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<>();
if(head != null) {
nodeQueue.add(head);
}
Node node = null;
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
node = nodeQueue.poll();
node.left = generateNode(queue.poll());
node.right = generateNode(queue.poll());
if(node.left != null) {
nodeQueue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
nodeQueue.add(node.right);
}
}
return node;
}
private static Node generateNode(String val) {
if(val == null) {
return null;
}
return new Node(val);
}
五、多叉树和二叉树互转
leetcode 431题 https://leetcode.com/problems/encode-n-ary-tree-to-binary-tree
一颗多叉树转为二叉树(所有的子节点都放在二叉树的左树的右边界上面),之后将二叉树转为之前的多叉树
// 将多叉数转尾二叉树
public static TreeNode encode(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(node.val);
treeNode.left = en(node.children);
return treeNode;
}
public static TreeNode en(List<Node> nodes) {
if(nodes == null || nodes.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
TreeNode head = null, current = null;
for (Node node : nodes) {
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(node.val);
// 记录头节点用于返回
if(head == null) {
head = treeNode;
} else {
// 将多叉节点一直往右放
current.right = treeNode;
}
current = treeNode;
// 将子多节点放到左边
current.left = en(node.children);
}
return head;
}
// 将二叉树转为多叉树
public static Node decode(TreeNode treeNode) {
if(treeNode == null) {
return null;
}
return new Node(treeNode.val, de(treeNode.left));
}
private static List<Node> de(TreeNode treeNode) {
if(treeNode == null) {
return null;
}
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (treeNode != null) {
// 创建节点,children就是所有的左子节点
Node current = new Node(treeNode.val, de(treeNode.left));
// 将所有的左节点放到list里面
list.add(current);
// 处理下一个节点
treeNode = treeNode.right;
}
return list;
}
六、设计一个打印整棵树的函数
跳过,可以自行实现
七、求二叉树最宽的层有多少个节点
按层遍历时,记录当前层的结束节点currentEnd, 下一层结束节点nextEnd。
使用Map
public static int maxWidthUseMap(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
// 记录所有节点的当前层数
Map<Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(head, 1);
int currentLevel = 1;
int levelNumber = 1;
int max = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node poll = queue.poll();
// 获取当前节点的层数
Integer level = map.get(poll);
if(poll.left != null) {
queue.add(poll.left);
map.put(poll.left, level + 1);
}
if(poll.right != null) {
queue.add(poll.right);
map.put(poll.right, level +1);
}
// 如果是同一个层级则增加当前层数数量
if(level == currentLevel) {
levelNumber++;
}
// 非同一个层级则遍历到了下一个层级,层级+1和获取最大层级数量
else {
currentLevel++;
max = Math.max(max, levelNumber);
levelNumber = 1;
}
}
return Math.max(levelNumber, max);
}
不使用Map
public static int maxWidth(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(node);
int max = 0;
int currentLevelNumber = 1;
Node currentRight = node;
Node nextRight = null;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node poll = queue.poll();
// 将左右节点放入队列,并赋值最右边的节点
if(poll.left != null) {
queue.add(poll.left);
nextRight = poll.left;
}
if(poll.right != null) {
queue.add(poll.right);
nextRight = poll.right;
}
currentLevelNumber++;
// 如果弹出的节点是下一个节点的最右节点,则初始化数据后进行下一层数量统计
if(poll == currentRight) {
max = Math.max(max, currentLevelNumber);
currentLevelNumber = 0;
currentRight = nextRight;
}
}
return max;
}
八、找到节点的后继节点
在中序遍历中,当前节点x的下一个节点就是后继节点
1、如果x存在右节点,那么x的后继节点就是右节点的最左节点。(右树上的最左)
2、如果x不存在右节点,则x不断往上找父节点,直到找到存在左孩子,则左孩子就是x的后继节点。(当前节点是父节点的左孩子)
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return node;
}
if(node.right != null) {
Node right = node.right;
while (right.left != null) {
right = right.left;
}
return right;
} else {
Node parent = node.parent;
// 当前节点是其父节点的右孩子
while (parent != null && parent.right == node) {
node = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
九、二叉树折纸问题
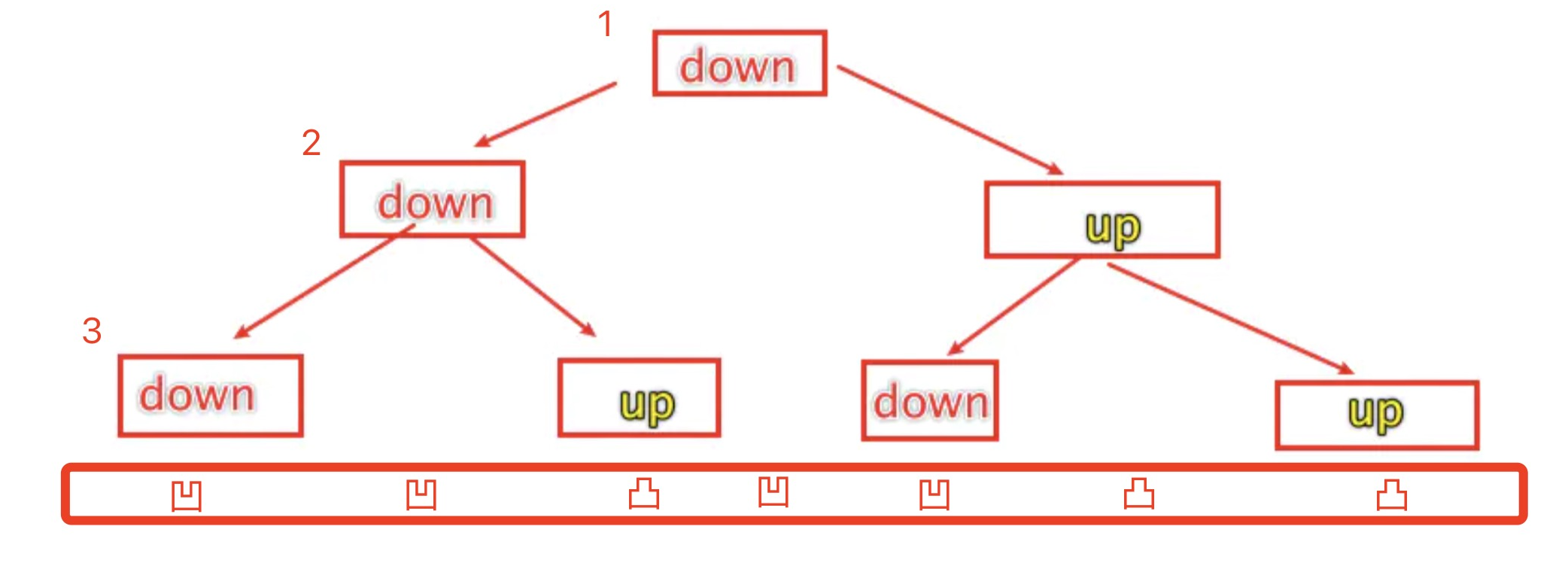
1、头节点是凹的
2、所有左节点是凹,右节点是凸
3、打印按照层数打印就是中序遍历
public static void paperFolding(int n) {
process(1, n, true);
}
/**
* true: down
* false:up
* i: 当前层数
* n:所有层数
* 中序遍历整棵树
*/
public static void process(int i, int n, boolean down) {
if(i > n) {
return;
}
process(i + 1, n, true);
System.out.println(down ? "down" : "up");
process(i + 1, n, false);
}
九、判断是否为完全二叉树
1、按层遍历,有右无左则返回false。
2、当第一次遇到没有左右子节点时,剩余节点也必须没有左右子节点
/**
* 判断是否为满二叉树,非递归版
*/
public static boolean isFull(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return false;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(node);
boolean exist = false;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node poll = queue.poll();
Node l = poll.left;
Node r = poll.right;
// 左孩子为空,右孩子不为空则不是
if(l == null && r != null) {
return false;
}
// 第二次遇到还有null的子节点
if(exist && (l != null || r != null)) {
return false;
}
if(l != null) {
queue.add(l);
}
if(r != null) {
queue.add(r);
}
// 第一次遇到没有子节点
if(l == null || r == null) {
exist = true;
}
}
return true;
}
十、判断是否为平衡树
所有会出现的情况
1、每一颗子树的左右高度相差的绝对值不超过1
2、左树、右树都必须是平衡二叉树
代码实现
// 判断是否为平衡二叉树
public static boolean isBalanced(Node node) {
return process(node).isBalanced;
}
public static Info process(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return new Info(true, 0);
}
Info l = process(node.left);
Info r = process(node.right);
// 计算当前层数
int max = Math.max(l.height, r.height) + 1;
// 其中一个子节点不是平衡二叉树则当前数不是平衡二叉树
if(!l.isBalanced || !r.isBalanced) {
return new Info(false, max);
}
// 左右子节点高度相差超过1
if(Math.abs(l.height - r.height) > 1) {
return new Info(false, max);
}
return new Info(true, max);
}
十一、判断是否为搜索二叉树
所有会出现的情况
1、头节点左子节点的值都比它小,右子节点的值都比它大
2、左树、右树都必须是搜索二叉树
3、经典二叉树没有重复值
代码实现
方式一:将二叉树用中序遍历,之后判断是否为逆序即可
public static boolean isSearchIn(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return true;
}
List<Node> list = new LinkedList<>();
// 利用中序将数据放到list里面
in(node, list);
for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) {
// 如果存在前面的数大于后面的数则非搜索树
if(list.get(i).value <= list.get(i -1).value) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void in(Node node, List<Node> list) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
in(node.left, list);
list.add(node);
in(node.right, list);
}
方式二:利用递归判断
public static boolean isSearch(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return true;
}
return process(node).isSearch;
}
public static Info process(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
Info l = process(node.left);
Info r = process(node.right);
// 获取左右孩子的最大最小值
int max = node.value;
int min = node.value;
if(l != null) {
max = Math.max(max, l.max);
min = Math.min(min, l.min);
}
if(r != null) {
max = Math.max(max, r.max);
min = Math.min(min, r.min);
}
// 左右孩子其中一个非搜索
if((l != null && !l.isSearch) || (r != null && !r.isSearch)) {
return new Info(false, max, min);
}
// 左边的值大于等于当前值 或者 右边的值小于当前值
if((l != null && l.max >= node.value) || (r != null && r.min <= node.value)) {
return new Info(false, max, min);
}
return new Info(true, max, min);
}
public static class Info{
public boolean isSearch;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(boolean isSearch, int max, int min) {
this.isSearch = isSearch;
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
}
}
十二、返回整颗二叉树节点与节点间的最大距离
所有会出现的情况
1、节点可能不经过头节点
- 二叉树左树和右树的最大的距离
2、会经过头节点的最大距离
- 左树最远(左高)+右树最远(右高)+1
代码实现
public static int getMaxDistance(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
return process(node).maxDistance;
}
private static Info process(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
Info l = process(node.left);
Info r = process(node.right);
// 获取最孩子和右孩子的最大高度
int height = Math.max(l.height, r.height) + 1;
// 最孩子的高度+右孩子的高度就是头节点最大距离
int headDistance = l.height + r.height + 1;
// 头节点、左孩子最大距离、右孩子最大距离的最大距离
int maxDistance = Math.max(l.maxDistance, Math.max(r.maxDistance, headDistance));
return new Info(maxDistance, height);
}
十三、满二叉树
数的高度是h, 那2^h -1 = 节点数
public static boolean isFull(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return true;
}
Info info = process(node);
return (1 << info.height) - 1 == info.nodeSize;
}
private static Info process(Node node) {
if(node == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
Info l = process(node.left);
Info r = process(node.right);
int height = Math.max(l.height, r.height) + 1;
int nodes = l.nodeSize + r.nodeSize + 1;
return new Info(height, nodes);
}
private static class Info{
public int height;
public int nodeSize;
public Info(int h, int n) {
this.height = h;
this.nodeSize = n;
}
}
// 第二种方法
// 收集子树是否是满二叉树
// 收集子树的高度
// 左树满 && 右树满 && 左右树高度一样 -> 整棵树是满的
public static class Info2 {
public boolean isFull;
public int height;
public Info2(boolean f, int h) {
isFull = f;
height = h;
}
}
十四、找到二叉树中最大的搜索二叉树
给定二叉树的子树是搜索二叉树的节点数最大值是多少,子二叉树必须是整棵树。
所有会出现的情况
1、头节点不是搜索二叉树
- 左树上的搜索二叉树的最多节点数
- 右树上的搜索二叉树的最多节点数
2、头节点是搜索二叉树
- 整个树的节点数
代码实现
public static int getLargestBSTSubtree(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
return process(node).maxSubtreeSize;
}
public static Info process(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) {
return null;
}
Info l = process(node.left);
Info r = process(node.right);
int allSize = 1;
int max = node.val;
int min = node.val;
// 左节点不为空,则获取所有节点数量、最大值、最小值
if(l != null){
allSize += l.allSize;
max = Math.max(max, l.max);
min = Math.min(min, l.min);
}
// 右节点不为空,则获取所有节点数量、最大值、最小值
if(r != null) {
allSize += r.allSize;
max = Math.max(max, r.max);
min = Math.min(min, r.min);
}
// 获取左节点是否为搜索树、左节点最大搜索树节点数
int p1 = -1;
boolean leftBST = true;
if(l != null){
p1 = l.maxSubtreeSize;
leftBST = l.maxSubtreeSize == l.allSize;
}
// 获取右节点是否为搜索树、右节点最大搜索树节点数
int p2 = -1;
boolean rightBST = true;
if(r != null) {
p2 = r.maxSubtreeSize;
rightBST = r.maxSubtreeSize == r.allSize;
}
// 如果左右两边都是搜索树
int p3 = -1;
if(leftBST && rightBST) {
int leftMax = l == null ? 0 : l.max;
int rightMin = r == null ? 0 : r.min;
// 如果整颗树都是搜索二叉树,则最大搜索树的节点树=左树节点树+右树节点树+1
if(leftMax < node.val && rightMin > node.val) {
p3 =(r== null ? 0 : r.maxSubtreeSize) + (l == null ? 0 : l.maxSubtreeSize) + 1;
}
}
return new Info(Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)), allSize, max, min);
}
public static class Info{
public int maxSubtreeSize;
public int allSize;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(int maxSubtreeSize, int allSize, int max, int min) {
this.maxSubtreeSize = maxSubtreeSize;
this.allSize = allSize;
this.max = max;
this.min = min;
}
}
// 提交时不要提交这个类
public static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int value) {
val = value;
}
}
另外一题是返回头节点,其他条件一样
十五、给定头节点和AB两个节点求AB两个最初公共祖先
a节点和b接口往上找汇聚的第一个节点
所有会出现的情况
1、汇聚的节点不是头节点
- 已经在左树上汇聚了
- 已经在右树上汇聚了
- a和b都没有找全
2、汇聚的节点是头节点
- 左树发现一个、右树发现另一个
- 头节点本身就是a节点,左树右树发现了节点b
- 头节点本省就是b节点,左树右树发现了节点a
3、上面的情况都没有匹配上则没有公共祖先
每个数需要的信息
1、树上有没有发现a
2、树上有没有发现b
3、树上发现的最低公共祖先(答案)
代码实现
private static Info process(Node head, Node a, Node b) {
if(head == null) {
return new Info(false, false, null);
}
Info l = process(head.left, a, b);
Info r = process(head.right, a, b);
// 头节点是a 或者 左右节点找到a
boolean findA = (head == a) || l.findA || r.findA;
// 头节点是b 或者 左右节点找到b
boolean findB = (head == b) || l.findB || r.findB;
Node ans = null;
if(l.ans != null) {
ans = l.ans;
} else if(r.ans != null) {
ans = r.ans;
} else {
// 左右都没有找到汇聚节点,但是左边和右边都找到了值,则头节点就是汇聚节点
if(findA && findB) {
ans = head;
}
}
return new Info(findA, findB, ans);
}
private static class Info{
private boolean findA;
private boolean findB;
private Node ans;
public Info(boolean findA, boolean findB, Node ans) {
this.findA = findA;
this.findB = findB;
this.ans = ans;
}
}
十六、派对的最大快乐值
公司现在要办party,你可以决定哪些员工来,哪些员工不来,规则:
如果某个员工来了,那么这个员工的所有直接下级都不能来
派对的整体快乐值是所有到场员工快乐值的累加
你的目标是让派对的整体快乐值尽量大给定一棵多叉树的头节点boss,请返回派对的最大快乐值。
所有会出现的情况
1、 当前节点参加派对
- 当前节点的快乐值+sum(子节点不参加派对的快乐值)
2、当前节点不参加派对
- sum(max(子节点参加派对的快乐值, 子节点不参加派对的快乐值))
需要的参数:参加派对的快乐值、不参加派对的快乐值
代码实现
private static Info process(Employee e) {
if(e == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
int yes = e.happy;
int no = 0;
for (Employee next : e.nexts) {
Info process = process(next);
// 当前节点不参加 = sum(max(yes,no))
no += Math.max(process.yes, process.no);
// 当前节点参加=sum(子节点不参加的快乐值)
yes += process.no;
}
return new Info(yes, no);
}
private static class Info{
public int yes;
public int no;
public Info(int yes, int no) {
this.yes = yes;
this.no = no;
}
}