07_图
一、基础
1.1 类型(按照方向区分)
有向图:有方向的图
无向图:无方向的图
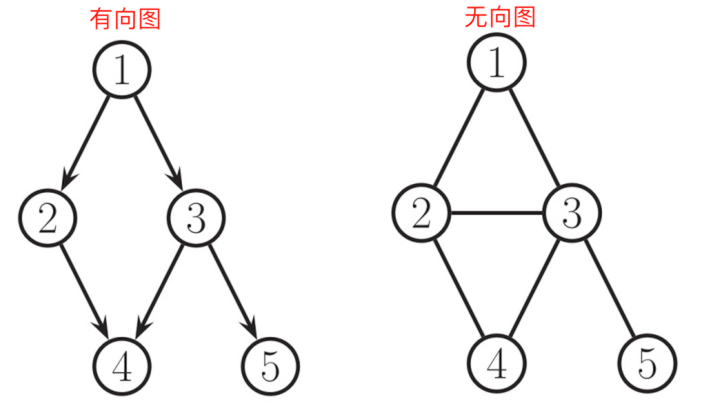
所有的无向图都可以转换为有向图,无向图相当于互相指的有向图
1.2 表达方式(存储结构)
邻接表法
记录当前节点的所有邻居
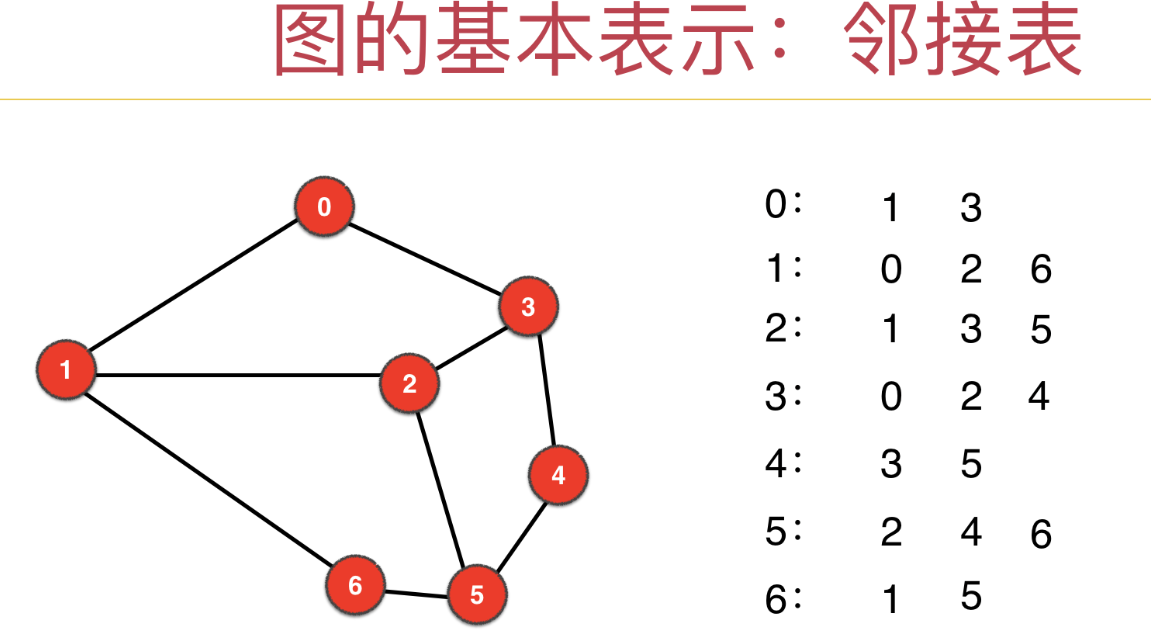
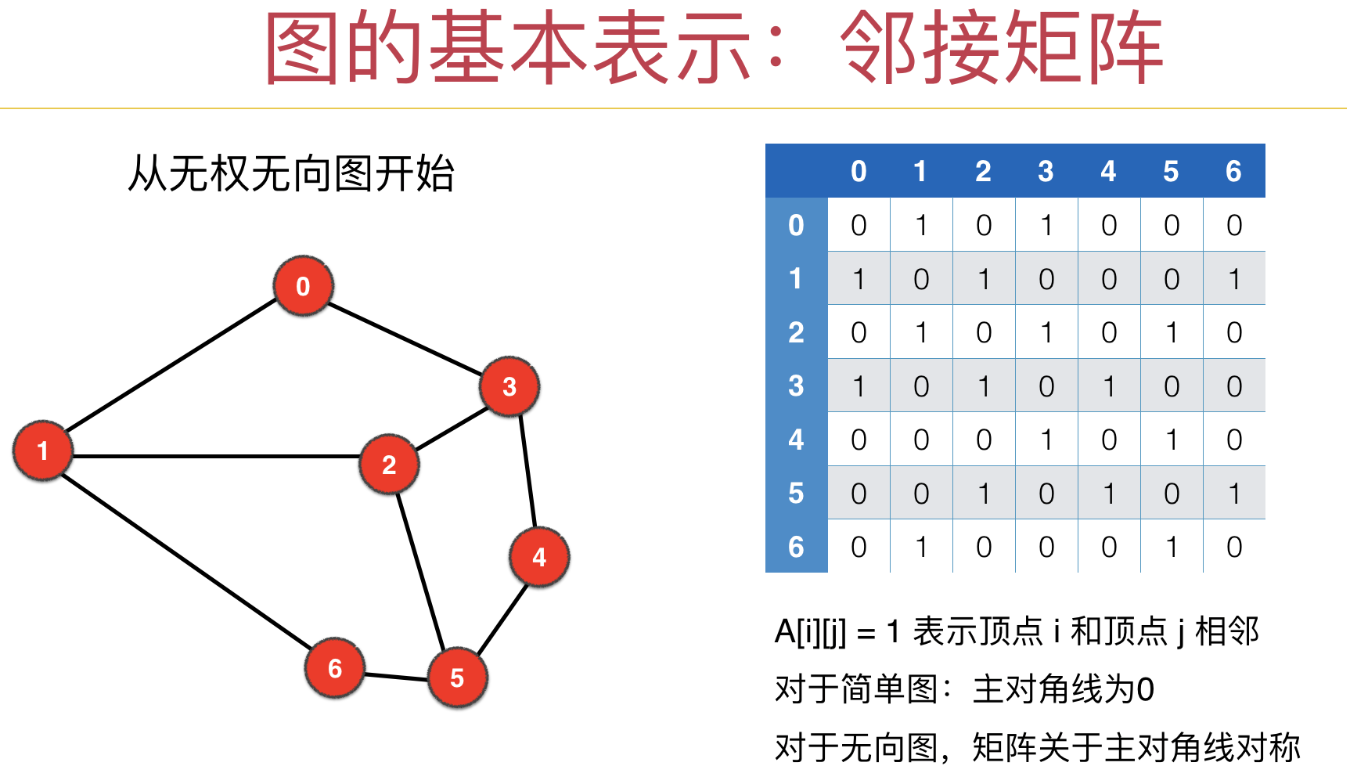
邻接矩阵法
利用矩阵的下标对应当前节点和其他节点是否相邻,相邻记录1或者权重
其他
二维矩阵表达(最常见):如{{2,3,4},{2,1,4}},表示3到4的权重是2,1到4的权重也是2。
单个数组(单向):如[3,1,0,2],表示0指向3,1指向1,2指向0,3指向2
图的解题方式:图有很多种数据结构去存储,如果每种数据结构都去写一遍代码那样的工作量是巨大的。可以自己抽象出一种数据结构去处理图数据,后面遇到图的问题就只需要写一个转换为当前数据结构的程序即可解题(适配器解决各种数据结构的代码编写)。
1.3 名词
- 入度:有向图顶点被指向的箭头个数
- 出度:顶点指出去的箭头个数
二、抽象结构
一个图包含节点和边对象(图对象、节点对象、边对象)。图对象里面利用hashmap存储节点和节点对象的对应关系以及所有的边节点,节点对象的元素有当前值、连接到当前节点的数量、连接出去的节点数量、连接出去的节点列表、连接出去的边,边对象的元素有权重和开始指向的节点、最终指向的节点。
// 存储所有的节点映射关系
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;
// 记录所有的边
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
this.nodes = new HashMap<>();
this.edges = new HashSet<>();
}
// 通过矩阵生成图
public static Graph createGraph(int[][] matrix) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int[] ints : matrix) {
int weight = ints[0];
int from = ints[1];
int to = ints[2];
// 将节点加入到节点列表
if(!graph.nodes.containsKey(from)) {
graph.nodes.put(from, new Node(from));
}
if(!graph.nodes.containsKey(to)) {
graph.nodes.put(to, new Node(to));
}
// 获取节点
Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(from);
Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(to);
// 边数据封装
Edge edge = new Edge();
edge.from = fromNode;
edge.to = toNode;
edge.weight = weight;
// from数据封装
fromNode.out++;
fromNode.nexts.add(toNode);
fromNode.edges.add(edge);
toNode.in++;
// 边是整个边的一部分
graph.edges.add(edge);
}
return graph;
}
public static class Node{
// 当前节点的值
public int value;
// 连接到当前节点的数量
public int in;
// 连接出去的节点数量
public int out;
// 连接出去的节点列表
public ArrayList<Node> nexts;
// 连接出去的边
public ArrayList<Edge> edges;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
this.in = 0;
this.out = 0;
this.nexts = new ArrayList<>();
this.edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
// 边
private static class Edge{
// 权重
public int weight;
public Node from;
public Node to;
}
三、遍历
3.1 宽度优先遍历(BFS)
用队列(先进先出)实现
// 遍历的时候必须要用set标记是否已经遍历过,节点可能往回指
public static void breathFirst(Graph.Node node) {
Queue<Graph.Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<Graph.Node> set = new HashSet<>();
queue.add(node);
set.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Graph.Node poll = queue.poll();
System.out.println(poll.value);
for (Graph.Node next : poll.nexts) {
if(!set.contains(next)) {
queue.add(next);
set.add(next);
}
}
}
}
3.2 深度优先遍历(DFS)
用栈(先进后出去)实现
// 深度优先遍历
public static void depthFirst(Graph.Node node) {
// 栈就是深度遍历的整条路径
Stack<Graph.Node> stack = new Stack<>();
HashSet<Graph.Node> set = new HashSet<>();
stack.push(node);
set.add(node);
System.out.println(node.value);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Graph.Node pop = stack.pop();
for (Graph.Node next : pop.nexts) {
if(!set.contains(next)) {
// 将弹出的节点重新压入
stack.push(pop);
stack.push(next);
set.add(next);
System.out.println(next.value);
// 打印后弹出
break;
}
}
}
}
四、题目(拓扑序)
拓扑排序一定是有向无环图
4.1 图的拓扑排序算法
一直将连接到当前节点(入度)的数量为0的节点作为头,头节点就是排序的顶节点
public static List<Graph.Node> sortedTopology(Graph graph) {
HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
Queue<Graph.Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 将所有的入度放入hashmap,如果入度为0就放入到队列中
graph.nodes.forEach((k,v) -> {
hashMap.put(v, v.in);
if(v.in == 0) {
queue.add(v);
}
});
List<Graph.Node> result = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Graph.Node poll = queue.poll();
result.add(poll);
// 遍历后面的节点列表,如果先将节点减一后。判断节点数为0就放入队列
for (Graph.Node next : poll.nexts) {
hashMap.put(next, hashMap.get(next) - 1);
if(hashMap.get(next) == 0) {
// 放入队列的节点就是排序后的节点
queue.add(next);
}
}
}
return result;
}
4.2 不同数据结果的拓扑排序一
1、利用动态规划的思想(记忆化思想)将数据存在map中,利用“点次”判断
2、将存在map中的值放入list中排序
3、排序中的节点返回即可
// 图排序
public static ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> topSort(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph) {
// 通过动态规划将每个节点以及节点的数量放到map里面
HashMap<DirectedGraphNode, Record> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (DirectedGraphNode directedGraphNode : graph) {
getRecord(directedGraphNode, hashMap);
}
// 通过数量进行排序
List<Record> records = new ArrayList<>();
for (Record value : hashMap.values()) {
records.add(value);
}
records.sort((a, b) -> {
return a.nodes == b.nodes ? 0 : (a.nodes > b.nodes ? -1 : 1);
});
// 排序后的节点就是图的排序
ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Record record : records) {
result.add(record.node);
}
return result;
}
// 通过递归获取点数
private static Record getRecord(DirectedGraphNode node, Map<DirectedGraphNode, Record> map) {
// 通过动态规划如果已经存在则直接获取
if(map.containsKey(node)) {
return map.get(node);
}
// 计算点数
long nums = 0;
for (DirectedGraphNode neighbor : node.neighbors) {
nums += getRecord(neighbor, map).nodes;
}
// 封装数据后返回
Record record = new Record(node, nums + 1);
map.put(node, record);
return record;
}
4.3 不同数据结果的拓扑排序二
项目是通过节点数,通过拓扑序的深度也可以排序。
private static class Record{
private DirectedGraphNode node;
private int deep;
public Record(DirectedGraphNode node, int deep) {
this.node = node;
this.deep = deep;
}
}
// 图排序
public static ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> topSort(ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> graph) {
// 通过动态规划将每个节点以及节点的数量放到map里面
HashMap<DirectedGraphNode, Record> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (DirectedGraphNode directedGraphNode : graph) {
getRecord(directedGraphNode, hashMap);
}
// 通过数量进行排序
List<Record> records = new ArrayList<>();
for (Record value : hashMap.values()) {
records.add(value);
}
records.sort((a, b) -> (b.deep - a.deep));
// 排序后的节点就是图的排序
ArrayList<DirectedGraphNode> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Record record : records) {
result.add(record.node);
}
return result;
}
// 通过递归获取点数
private static Record getRecord(DirectedGraphNode node, Map<DirectedGraphNode, Record> map) {
// 通过动态规划如果已经存在则直接获取
if(map.containsKey(node)) {
return map.get(node);
}
// 计算点数
int deep = 0;
for (DirectedGraphNode neighbor : node.neighbors) {
deep = Math.max(deep, getRecord(neighbor, map).deep);
}
// 封装数据后返回
Record record = new Record(node, deep + 1);
map.put(node, record);
return record;
}
4.4 生成最小树算法kruskal
无向图
思路:贪心和并查集完成
1、从最小的表开始检查,一次检查变大的边
2、当前边进入最小生成树的集合会形成环则要当前边,否则不要。
3、检查完成最小生成树的集合就获取了
public static Set<Graph.Edge> kruskalMST(Graph graph) {
// 创建并查集并初始化
UnionSet unionSet = new UnionSet();
unionSet.makeSets(graph.nodes.values());
// 将所有的边放入优先级队列
PriorityQueue<Graph.Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {
return a.weight - b.weight;
});
for (Graph.Edge edge : graph.edges) {
queue.add(edge);
}
Set<Graph.Edge> set = new HashSet<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 获取最小的边
Graph.Edge poll = queue.poll();
// 如果边的两端不再一个集合则将当前边就是结果值
if(!unionSet.isSame(poll.from, poll.to)) {
set.add(poll);
// 合并当前边
unionSet.union(poll.from, poll.to);
}
}
return set;
}
public static class UnionSet{
private HashMap<Graph.Node, Graph.Node> father;
private HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> sizes;
public UnionSet() {
father = new HashMap<>();
sizes = new HashMap<>();
}
private Graph.Node findFather(Graph.Node node) {
Stack<Graph.Node> stack = new Stack<>();
while (node != father.get(node)) {
stack.add(node);
node = father.get(node);
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
father.put(stack.pop(), node);
}
return node;
}
// 初始化节点
public void makeSets(Collection<Graph.Node> nodes) {
father.clear();
sizes.clear();
for (Graph.Node node : nodes) {
father.put(node, node);
sizes.put(node, 1);
}
}
public boolean isSame(Graph.Node a, Graph.Node b) {
Graph.Node aNode = findFather(a);
Graph.Node bNode = findFather(b);
return aNode == bNode;
}
public void union(Graph.Node a, Graph.Node b) {
Graph.Node aNode = findFather(a);
Graph.Node bNode = findFather(b);
if(aNode != bNode) {
int aLength = sizes.get(aNode);
int bLength = sizes.get(bNode);
if(aLength > bLength) {
father.put(bNode, aNode);
sizes.put(aNode, aLength + bLength);
sizes.remove(bNode);
} else {
father.put(aNode, bNode);
sizes.put(bNode, aLength + bLength);
sizes.remove(aNode);
}
}
}
}
4.5生成最小树算法prim
无向图
思路:
1、从任意节点出发寻找最小生成树
2、节点加入到被选中节点后,解锁点出发的所有新边
3、解锁边中选择最小的表,看边是否形成环(往后指向的节点在选中节点中就会形成环)
4、会:不要当前边,继续检查解锁的其他最小表,重复3
5、不会:要当前边,将边指向点加入到解锁节点中
6、所有点都被选取,就获得了最小生成树
public static Set<Graph.Edge> primMST(Graph graph) {
// 创建优先级队列,小根堆。每次获取最小边
PriorityQueue<Graph.Edge> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {
return a.weight - b.weight;
});
// 存储解锁的选中节点,防止往回走
Set<Graph.Node> nodes = new HashSet<>();
// 存储选中的边
Set<Graph.Edge> result = new HashSet<>();
for (Graph.Node node : graph.nodes.values()) {
nodes.add(node);
// 点解锁所有的边
for (Graph.Edge edge : node.edges) {
queue.add(edge);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 优先处理解锁边里面最小的边
Graph.Edge poll = queue.poll();
// 解锁往后指向的节点,并判断节点是否是新的节点
Graph.Node to = poll.to;
if(!nodes.contains(to)) {
// 不是新节点则将节点放入解锁列表,以及放入选中表
nodes.add(to);
result.add(poll);
// 将其他边放入优先级队列
for (Graph.Edge edge : to.edges) {
queue.add(edge);
}
}
}
// 防止森林
// break;
}
return result;
}
4.6 迪瑞克斯拉算法dijkstra
思路:
1、有向无负权重图,可以有环。一定有一个给定节点。 最短距离,如地图获取最短路径。
2、生成一个源点到各个点的最小距离表,开始记录一条源点到自己距离为0,到其他源点距离为正无穷大。
3、从距离表中取出没有选中过的最小边节点,更新源点到各个点之间的最小距离,不断重复
4、源点到所有点记录都被选中,则获取到了最小距离表
/**
* 获取图的最小距离表
*/
public static HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> getDijkstra(Graph.Node node) {
// 创建距离表
HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 创建选中表
Set<Graph.Node> selected = new HashSet<>();
map.put(node, 1);
// 获取最小节点,第一次就是当前节点
Graph.Node minNode = getMinNode(map, selected);
if(minNode != null) {
// 获取当前节点的最小距离
Integer distance = map.get(minNode);
// 遍历所有的边
for (Graph.Edge edge : minNode.edges) {
// 如果当前边在距离表中不存在,则存入距离表,距离=当前节点最小距离+当前边距离
Graph.Node to = edge.to;
Integer currentDistance = distance + edge.weight;
if(!map.containsKey(edge)) {
map.put(to, currentDistance);
}
// 在距离表中存在,则更新最小距离
else {
map.put(to, Math.min(map.get(to), currentDistance));
}
}
// 将最小距离节点标记为选中
selected.add(minNode);
// 获取下一个选中距离
minNode = getMinNode(map, selected);
}
return map;
}
/**
* 在距离表中获取没有选中过的最小距离的节点
*/
private static Graph.Node getMinNode(HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> map, Set<Graph.Node> selected) {
Integer min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Graph.Node minNode = null;
for (Map.Entry<Graph.Node, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
Integer distance = entry.getValue();
Graph.Node node = entry.getKey();
if(!selected.contains(node) && distance < min) {
minNode = node;
min = distance;
}
}
return minNode;
}
4.6 迪瑞克斯拉算法dijkstra(优化)
1、利用堆去优化getMinNode方法的来回遍历
2、系统的堆无法改变值后在调整位置,故用改进的加强对可以实现。
/**
* 获取图的最小距离表(代码未验证是否正确)
* 1、将元素都放入小根堆
* 2、依次弹出数据的值就是距离表的数据,逐个处理每个节点的边
* - 存在就更新最小的距离
* - 不存在就插入元素
*/
public static HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> getDijkstra(Graph.Node node, int size) {
// 创建加强堆,并将节点放入到堆中
NodeHeap nodeHeap = new NodeHeap(size);
HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> result = new HashMap<>();
nodeHeap.addOrUpdate(node, 0);
// 堆不为空则处理数据
if(!nodeHeap.isEmpty()) {
RecordNode record = nodeHeap.pop();
Graph.Node rNode = record.node;
Integer rDistance = record.distance;
// 处理节点的所有边
for (Graph.Edge edge : rNode.edges) {
// 添加或者更新堆的最小距离
nodeHeap.addOrUpdate(edge.to, rDistance + edge.weight);
}
result.put(rNode, rDistance);
}
return result;
}
// 小根堆
public static class NodeHeap{
// 数组存放堆
private Graph.Node[] nodes;
// 堆下标映射, 反向索引表
private HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> heapIndexMap;
// 距离映射
private HashMap<Graph.Node, Integer> distanceMap;
private int size;
public NodeHeap(int size) {
this.nodes = new Graph.Node[size];
this.heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
this.distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
this.size = 0;
}
public void addOrUpdate(Graph.Node node, int distance) {
// 在堆里面,进行更新
if(inHeap(node)) {
distanceMap.put(node, Math.min(distance, distanceMap.get(node)));
insertHeapify(heapIndexMap.get(node));
}
if(!isEntered(node)) {
// 将值放到最后面
nodes[size] = node;
heapIndexMap.put(node, size);
distanceMap.put(node, distance);
insertHeapify(size++);
}
}
// 插入调整堆(上浮)
private void insertHeapify(Integer index) {
// 比较当前index的距离和父距离
while (distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[(index - 1) /2])) {
swap(index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 判断是否放入过堆中
public boolean isEntered(Graph.Node node) {
return heapIndexMap.containsKey(node);
}
// 判断是否在堆里面
public boolean inHeap(Graph.Node node) {
return isEntered(node) && heapIndexMap.get(node) != -1;
}
public RecordNode pop() {
RecordNode recordNode = new RecordNode(nodes[0], distanceMap.get(nodes[0]));
// 将最后面的值放在最前面
swap(0, size - 1);
// 将弹出的值下标置为-1
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[size - 1], -1);
distanceMap.remove(nodes[size - 1]);
nodes[size - 1] = null;
heapify(0, --size);
return recordNode;
}
// 下沉
private void heapify(int i, int size) {
int left = i * 2 + 1;
while (left < size) {
// 获取左右孩子中最小值的下标
int minVal = (left + 1) < size && distanceMap.get(nodes[left + 1])
< distanceMap.get(nodes[left]) ? left + 1 : left;
// 最小值和当前值获取最小的
minVal = distanceMap.get(nodes[minVal]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[i])
? minVal : i;
// i的距离就是最大的
if(minVal == i) {
break;
}
swap(minVal, i);
i = minVal;
// 计算左边的下标值
left = i * 2 +1;
}
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[i], j);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[j], i);
Graph.Node tmp = nodes[i];
nodes[i] = nodes[j];
nodes[j] = tmp;
}
}
private static class RecordNode{
public Graph.Node node;
public Integer distance;
public RecordNode(Graph.Node node, Integer distance) {
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}